Eating right and exercising are crucial to helping diabetics control their blood sugar levels and live healthy lives, but checking your blood sugar regularly is also important. Without knowing how much sugar you have in your bloodstream, you could miss out on the signs of high or low blood sugar and be unaware that they’re happening, which could lead to serious complications if left unchecked. By keeping tabs on your blood sugar level, you can take the necessary precautions to keep your body at the right temperature at all times. Here’s why checking your blood sugar is so important for diabetics.
How to Take a Glucose Test

No matter what type of diabetes you have, it’s crucial to keep an eye on your blood sugar levels and your HbA1c. Fortunately, it’s very easy to do so with a portable machine and a diabetic meter. The best way to make sure you’re receiving accurate results is to test your blood glucose levels once per day at roughly the same time. This will enable your doctor and doctor to determine if your treatment plan is effective for you! To get started, follow these steps:
To check your blood sugar level, you will prick your finger with a lancet or a needle made for diabetics. You can purchase these needles online or from most pharmacies. The next step is to apply pressure to the wound and squeeze out a single drop of blood. Once you have done this, move the needle on top of the diabetic meter to the small well and wait. If you’re using a Freestyle Lite Meter (which comes standard in many health insurance plans), use one drop of blood from each finger—if not, use two drops from one finger. Finally, wait 10 seconds for your glucose level to be displayed on screen before recording it in your journal or diary book.
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)

Both insulin pumps and CGMs allow you to measure your blood sugar with a portable machine. With these devices, you can read your levels every minute and administer insulin accordingly. While not all diabetics have access to these tools, those who do benefit tremendously from them. But even if you don’t have one of these devices available to you, it’s a good idea to check your blood sugar regularly (at least 4 times per day). Use a glucometer and use test strips that are easy on your wallet—just make sure that you properly calibrate and maintain your monitor!
Insulin pumps allow you to automatically administer insulin at regular intervals, and they also can provide supplemental boluses of insulin when needed. On top of that, some pumps also have alarms and sensors that can help alert you to changes in your blood sugar levels or impending highs or lows. Continuous glucose monitors, on the other hand, use a sensor that’s placed just under your skin to measure your blood sugar levels every few minutes. The data is then seen on a gadget attached to your wrist (connected wirelessly to your device), so you know what’s going on with your blood sugar at all times.
Why checking your blood sugar is so important
 If you suffer from diabetes, your body is unable to properly use insulin, a hormone that helps convert sugar in food into energy. The most common form of diabetes is type 2, which occurs when either your pancreas does not produce enough insulin or your body becomes resistant to it. When you eat food containing sugar (carbohydrates), your blood sugar levels increase. This prompts beta cells in your pancreas to release insulin into your bloodstream so it can do its job of helping glucose enter cells to be used as fuel. However, if you have type 2 diabetes and are not using an effective treatment plan, more glucose than normal enters cells, which causes high blood sugar levels.
If you suffer from diabetes, your body is unable to properly use insulin, a hormone that helps convert sugar in food into energy. The most common form of diabetes is type 2, which occurs when either your pancreas does not produce enough insulin or your body becomes resistant to it. When you eat food containing sugar (carbohydrates), your blood sugar levels increase. This prompts beta cells in your pancreas to release insulin into your bloodstream so it can do its job of helping glucose enter cells to be used as fuel. However, if you have type 2 diabetes and are not using an effective treatment plan, more glucose than normal enters cells, which causes high blood sugar levels.
What are some of the common symptoms of high blood sugar: One of the more common symptoms of high blood sugar is thirst, followed by increased urination, feelings of fatigue, and blurred vision. Left untreated, you may feel sleepy, get a stomachache, and feel like throwing up. Weight loss may also occur for those with high blood sugar. It’s because too much glucose can be converted into fat that’s stored in your body as triglycerides, and that excessive fat can eventually lead to insulin resistance and other problems.
Diabetes Management Tips For The Holidays

If you have diabetes, it can be tempting to take a break from keeping tabs on your blood sugar during major holidays and festivities. You might decide that testing your blood sugar or using insulin doesn’t matter while you’re surrounded by friends and family who care about you. While taking it easy is OK every once in a while, monitoring your blood sugar is important all year long – not just during special occasions. If you don’t monitor and manage your blood sugar levels, life-threatening complications can develop, including vision loss and heart disease.
When you’re handling diabetes, it can be easy to overlook some important information. Although your A1C and blood sugar levels can be affected by multiple factors, including diet and exercise, they are largely controlled by your medication. In order to keep your blood sugar stable and in line with medical advice – along with eating the foods you want and living life – you’ll need to keep up with your medication. Your diabetes may be of different types and according to that, your idea of perfect or normal blood sugar levels will also differ. It is possible that if you do not follow these guidelines, your current illness could get worse and spread to another illness.
Facts About Type 1 Diabetes
Approximately 1.25 million people in America have Type 1 diabetes. The disease is usually diagnosed during childhood or adolescence, although it can be diagnosed at any age. While some cases of Type 1 are idiopathic (meaning that no cause is known), most cases are genetically linked and passed on from parents to their children. For example, if one parent has Type 1 diabetes, each child has a 25% chance of inheriting it. If both parents have Type 1 diabetes, each child has a 50% chance of developing it themselves. That said, only 5-10% of all people with Type 1 diabetes are genetically predisposed to the disease. Most patients who develop Type 1 do so as a result of an autoimmune disorder that destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. It’s important to note that even though Type 2 diabetes is often called adult onset diabetes because it typically develops later in life, about 10% of new cases every year are actually adolescents who develop Type 2 after being overweight for several years but never having had high blood sugar levels before.
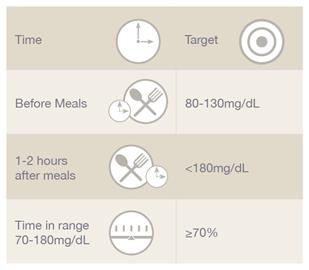
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that causes a person’s body to attack their own cells and makes them unable to produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood sugar levels, and without it patients with Type 1 diabetes have abnormally high blood sugar levels. In healthy people, when the blood sugar level rises and is greater than what is considered normal (around 80-120 mg/dL), insulin is released from the pancreas into the bloodstream in order to bring it back down to a normal level. Those with Type 1 diabetes don’t have beta cells in their pancreas and instead use injected synthetic insulin to keep their blood sugar levels steady through a process called carbohydrate counting.
What Are Carbohydrates?

Carbohydrates, which are found in plant-based foods like whole grains, fruits and vegetables, dairy products and beans, are a type of food that your body uses as its main source of energy. When you eat carbohydrates, for example in a slice of bread or an apple, your digestive system breaks down these foods into glucose (which is converted to sugar in your bloodstream). When it comes to managing glucose, one has a great deal of help from insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows glucose to enter the cells of the body. Without enough insulin, or when you have type 1 diabetes and can’t make any at all, glucose can’t get into cells and builds up in your blood instead.
Checking your blood sugar levels is an important way to maintain healthy levels of glucose in your blood.
When should you check it? There are two main times to check your blood sugar. First, many people with diabetes take a reading after eating a meal or snack to see how their body is responding to food and if their meals are providing them with enough energy.
So where do you need to test? It’s important that you know where your best spots are on your body for testing so that you can test without fail, whenever you need to. Devices such as blood sugar testing strips with longer stem lengths, finger lancets, and lancing devices are more convenient for those who have trouble reaching the affected area.